1. Introduction
Hiring bias has long been a problem, influencing who is given opportunities and who is passed over. Now that artificial intelligence (AI) is becoming more prevalent in hiring, the key question is whether AI can actually eliminate bias in hiring or if it just reflects human shortcomings in different ways.
2. What is Bias in Hiring?
Unfair or biased decisions made during the recruitment and selection process are referred to as bias in hiring. It happens when evaluations of candidates are influenced by preconceived notions, stereotypes, or personal opinions rather than just their abilities and potential. Bias frequently infiltrates hiring decisions, even in the presence of structured procedures.
The following are common sources of bias: academic background, where candidates from prestigious schools are given preference over equally capable individuals from lesser-known institutions; gender, where women may be evaluated more harshly for leadership roles; race and ethnicity, where certain names or backgrounds may face unconscious prejudice; and cultural assumptions, where behaviors, accents, or communication styles are incorrectly used as proxies for competence.
This is significant because bias affects organizations as well as individuals. Employers miss out on the opportunity to create diverse teams that foster innovation and creativity when talent is ignored. Diverse groups are consistently better at coming up with new ideas, solving complex problems, and adjusting to shifting market conditions, according to research.
Bias in hiring practices can impede the flow of new ideas for companies at the forefront of science, engineering, or technology. This diminishes competitiveness in addition to fairness. Companies that address hiring bias not only fulfill their legal and ethical commitments, but they also foster innovative environments.
To put it briefly, hiring bias is a barrier to advancement rather than just an HR issue.
3. How AI is Used in Hiring Today
Artificial intelligence has already made its way into multiple stages of the hiring process. Instead of relying solely on human recruiters, companies now use AI tools to sift through large applicant pools with speed and precision.
One common application is resume screening algorithms. These tools scan resumes for keywords, skills, and experiences that match job requirements. The goal is to save time and ensure that only qualified candidates move forward.
Next, video interview analysis tools use AI to assess candidates’ speech patterns, facial expressions, and body language. While controversial, these tools claim to identify communication skills, confidence, and even emotional intelligence.
Another use is predictive analytics for candidate success. AI systems analyze past hiring data to forecast which applicants are most likely to perform well in a given role. For example, if previous top performers share certain skills or experiences, AI may highlight candidates with similar profiles.
Finally, automated skill assessments allow candidates to complete online tests—ranging from technical problem-solving tasks to situational judgment exercises—scored instantly by AI. This gives recruiters more objective data to compare applicants.
Together, these tools aim to speed up decision-making, reduce recruiter workload, and provide more consistent evaluations. However, while AI promises efficiency, the key question is whether it can also deliver fairness. Can these systems truly filter out human bias, or do they simply replicate it in digital form?
Read more: AI in Recruitment – What Actually Works in 2025
4. Can AI Actually Remove Bias?
AI’s ability to process data consistently and emotionlessly holds promise for the hiring industry. Algorithms are not distracted, weary, or influenced by unimportant details like humans are. They are able to apply decision rules consistently, score interviews based on the same standards, and scan thousands of resumes. This consistency initially appears to be the ideal remedy for bias.
AI is also very good at identifying patterns. For instance, AI could determine the fundamental abilities that predict job success rather than concentrating on a person’s educational background. This might make it easier to find untapped talent from unconventional backgrounds.
The catch is that AI systems pick up knowledge from past data. The algorithm might reproduce biased hiring practices from the past, such as giving preference to men for technical positions.
This explains why the quality of training data is so important. Biased models will result from a dataset full of biased decisions. AI may still exclude competent applicants if it is not carefully designed, just because they don’t fit with traditional hiring practices.
Another difficulty is the “black box” issue. Because many AI models are intricate, it can be challenging for recruiters to comprehend the reasoning behind a decision. It can be challenging to explain a candidate’s rejection. This calls into question fairness and accountability.
Explainable AI (XAI) is useful in this situation. By displaying to candidates and recruiters the variables affecting results, XAI seeks to make AI decisions transparent. For instance, the system might indicate that a candidate’s skill set did not match the requirements of the position rather than just rejecting them.
Can bias be eliminated by AI, then? The response is complex. AI can lessen some forms of bias, particularly those related to subjective assessments, but it cannot completely eradicate bias without close supervision. The way AI is developed, trained, and observed determines how effective it is.
When used properly, AI can be a tool for equity. In its worst form, it runs the risk of turning into a high-tech version of the same old issues.

5. Types of Bias AI May Address
- Resume Bias
Traditional resume reviews often allow unconscious bias to creep in—such as assumptions based on names, schools, or job titles. AI tools can anonymize resumes, focusing only on skills, certifications, and experience. For example, instead of filtering out candidates with unfamiliar universities, AI could prioritize demonstrated achievements. - Interview Bias
Human interviewers sometimes judge candidates based on appearance, accents, or mannerisms. AI-driven interview platforms can standardize questions and evaluate responses consistently. While controversial, these tools may reduce subjective interpretation—though safeguards are needed to ensure they don’t introduce new forms of bias. - Performance Prediction Bias
Humans may assume that certain backgrounds predict better job performance, but AI can focus on measurable indicators instead—such as past project outcomes, problem-solving tests, or technical assessments. This shifts hiring from subjective impressions to evidence-based evaluation. - Cultural Fit Bias
Hiring for “culture fit” can exclude candidates who bring valuable diversity. AI systems can help balance this by identifying complementary skills and perspectives rather than enforcing conformity. Instead of asking, “Do they fit in?” the question becomes, “Can they add something new and useful?”
By targeting these areas, AI tools offer organizations a way to move toward fairer hiring decisions.
6. Benefits of Using AI in Hiring
When applied thoughtfully, AI brings several advantages to the hiring process:
- Consistency: AI evaluates candidates using the same standards, reducing the influence of mood, fatigue, or unconscious preferences.
- Scalability: AI can handle thousands of applications quickly, allowing companies to consider larger, more diverse talent pools.
- Objectivity: By focusing on data-driven factors like skills, test results, and measurable achievements, AI can shift the emphasis away from personal bias.
- Efficiency: Automating repetitive tasks frees recruiters to focus on relationship-building and strategic planning.
- Diversity Potential: If designed correctly, AI tools can help organizations expand their hiring reach and improve diversity outcomes by uncovering overlooked talent.
The benefits are clear—but they depend heavily on responsible implementation.
7. Challenges and Risks of AI in Hiring
While AI brings promise, it also introduces serious challenges.
- Data Bias
AI is only as good as the data it learns from. If historical hiring practices favored certain groups, the algorithm may carry that bias forward. For example, if past engineering hires were mostly men, the AI may incorrectly rank female candidates lower. - Algorithmic Transparency
Many AI systems operate like black boxes, making it difficult to understand why a candidate was rejected. Lack of clarity can undermine trust and raise questions about fairness. - Ethical Concerns
Even if AI reduces some biases, questions remain: Who is accountable when an algorithm makes a mistake? Is it ethical to judge candidates using automated systems that analyze facial expressions or speech? - Legal and Compliance Issues
Employment laws require fairness and non-discrimination. If an AI system unintentionally discriminates, companies could face lawsuits. Regulators are now scrutinizing AI hiring tools more closely, demanding compliance with evolving standards.
In short, while AI may speed up hiring, it also creates new risks that organizations must navigate carefully.
Read more: How To Remove Bias From AI Generated Job Postings
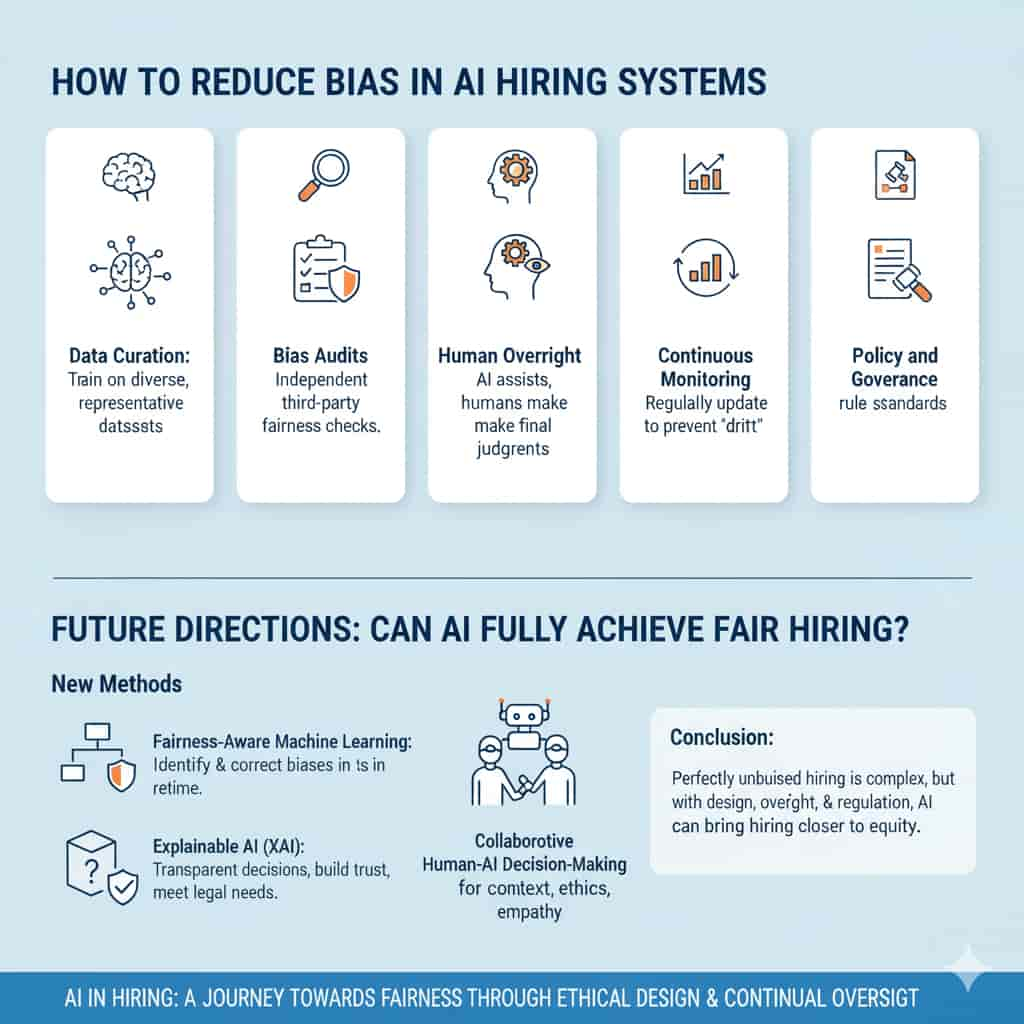
9. How to Reduce Bias in AI Hiring Systems
To harness AI’s potential while minimizing risks, organizations need proactive strategies:
- Data Curation
AI models should be trained on diverse, representative datasets. This means including candidates of different genders, races, and backgrounds to prevent skewed outcomes. - Bias Audits
Independent third-party audits can test AI tools for fairness and accuracy. Just as financial systems undergo regular audits, AI hiring systems need external checks. - Human Oversight
AI should assist—not replace—human judgment. Recruiters must review AI recommendations critically, ensuring that automation doesn’t override common sense or ethical considerations. - Continuous Monitoring
AI systems must be updated regularly. Over time, models can “drift,” meaning their predictions become less accurate or biased again. Monitoring ensures they stay aligned with fairness goals. - Policy and Governance
Clear rules and standards must guide how AI is used in hiring. Industry-wide governance frameworks can help set ethical boundaries and encourage best practices.
By combining technical safeguards with human responsibility, organizations can reduce the risk of biased AI hiring tools.
Read more: AI Tools for Small Business Cost-Effective: Complete Guide 2025
10. Future Directions: Can AI Fully Achieve Fair Hiring?
In order to make AI more equitable in the future, researchers are creating new techniques. Real-time bias detection and correction is the goal of debiasing algorithms and fairness-aware machine learning.
Another significant factor will be the emergence of explainable AI, which will provide candidates and recruiters with more precise information about choices. In addition to fostering trust, transparency assists organizations in adhering to legal obligations.
In the end, collaborative human–AI decision-making might be the way of the future. AI could manage data-intensive tasks rather than completely automating hiring, with humans contributing context, ethics, and empathy.
Will AI ever be able to hire people in an entirely objective manner? Most likely not, given how difficult it is to define “fairness.” However, AI has the potential to make hiring more equitable than ever before with the correct planning, supervision, and regulation.
11. Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can AI guarantee unbiased hiring decisions?
No. AI can reduce bias but not eliminate it entirely. The outcomes depend on the quality of data, design of the algorithm, and human oversight.
2. What types of bias are hardest for AI to eliminate?
Cultural and contextual biases are especially challenging. For example, judging communication styles or “fit” often involves subjective values that are hard to encode into data.
3. How do companies audit AI hiring tools for fairness?
Through third-party bias audits, fairness testing, and transparency reports. These audits check whether different groups of candidates are treated equally.
4. Is AI more reliable than human recruiters?
AI can be more consistent in applying criteria, but humans bring empathy and ethical judgment. The best results often come from combining both.
5. What role do regulations play in AI-driven hiring?
Regulations ensure companies use AI responsibly, preventing discrimination and protecting candidate rights. Emerging laws are pushing for greater transparency and accountability.
6. Can AI improve diversity hiring outcomes?
Yes—when designed with fairness in mind. AI can help identify talent from underrepresented groups that might otherwise be overlooked.
7. How does biased data impact AI recruitment tools?
Biased data can lead AI to replicate unfair patterns. For example, if past hires favored one group, AI may rank similar candidates higher, excluding others unfairly.
8. Should hiring decisions ever be fully automated?
No. While AI can assist in filtering and evaluation, final hiring decisions should always involve human judgment to ensure fairness and accountability.
9. What are the ethical concerns with AI in hiring?
Key concerns include candidate privacy, accountability for algorithmic errors, and whether it’s fair to judge people using automated analysis of voice or facial expressions.
10. How will AI hiring systems evolve over the next decade?
We can expect more transparency, better debiasing tools, and stronger regulations. AI will likely act as a partner to human recruiters rather than replacing them entirely.


1 thought on “Can AI Remove Bias in Hiring? Best Insights 2025”