Introduction
Our content creation process has been revolutionized by artificial intelligence, which has made it faster and more scalable than ever. However, success is not assured by speed alone. Businesses must guarantee accuracy, consistency, and reliability if they want to reap the full benefits. A well organized AI content quality assurance (QA) procedure can help with that.
What is AI Content Quality Assurance?
The systematic process of examining, assessing, and improving content created by artificial intelligence systems is known as AI content quality assurance, or QA. It guarantees that the information is factually correct, pertinent, and consistent with brand standards in addition to being grammatically correct.
Consider artificial intelligence (AI) as a high-speed printing press that can produce content indefinitely. However, in the absence of supervision, that content might be rife with mistakes, contradictions, or inaccuracies. QA bridges the gap between human expectations and machine efficiency by serving as an editor, fact checker, and brand guardian all in one.
Fundamentally, AI content QA entails:
- Accuracy checks: Ensuring claims, statistics, and references are factually correct.
- Consistency audits: Verifying tone, style, and formatting match brand guidelines.
- Audience alignment: Confirming the piece resonates with the intended readers and serves the right purpose.
- Compliance checks: Making sure the content adheres to legal, ethical, and organizational standards.
AI QA must also handle particular problems like “hallucinations,” in which AI confidently produces false information, in contrast to traditional QA for human-written content. The propensity of AI to generate generic, repetitive, or off-brand text presents another difficulty.
An efficient AI content QA procedure proactively creates safeguards rather than reactively fixing issues as they arise. This entails developing automated checks, workflows, and benchmarks that assist in locating and resolving problems before they jeopardize confidence. In actuality, it involves combining human judgment with intelligent tools to produce content that is impactful, dependable, and quick.
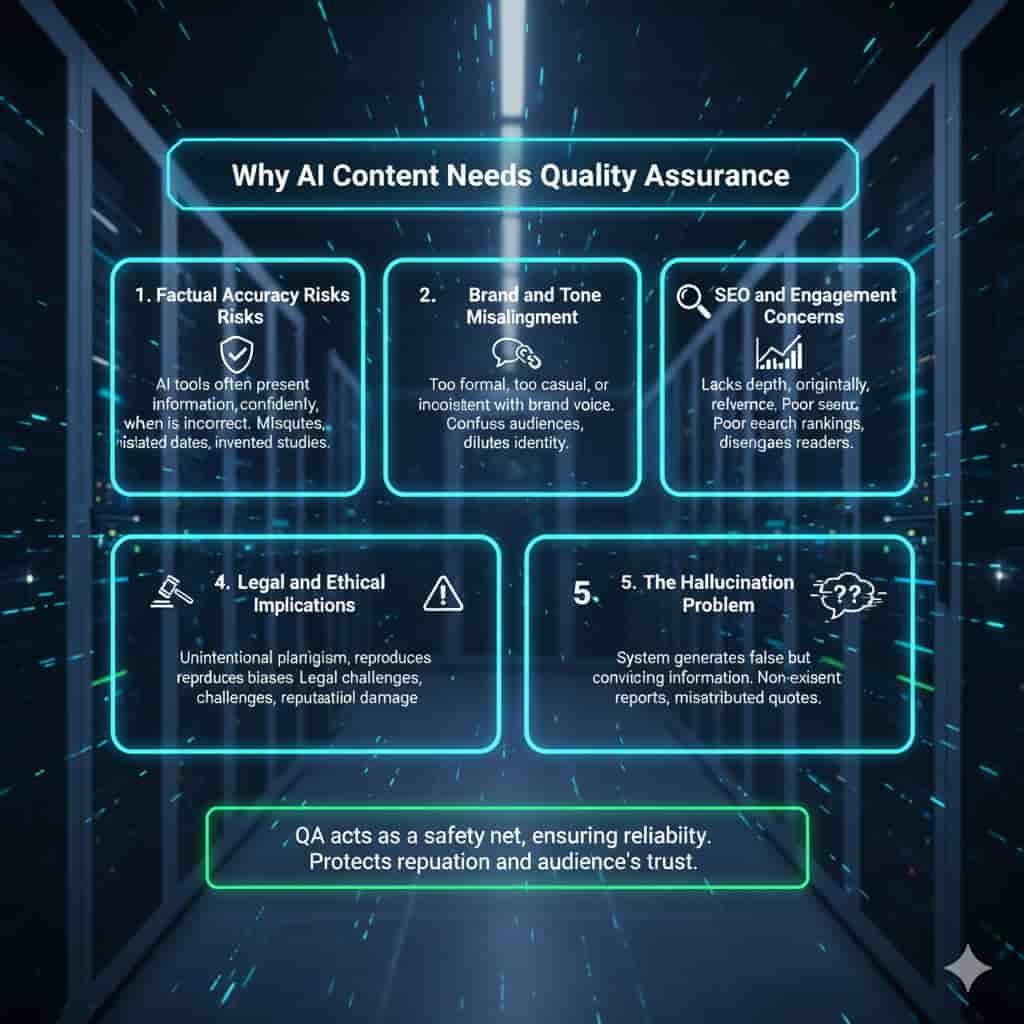
Why AI Content Needs Quality Assurance
AI generated content is strong, but it has flaws. AI depends on patterns found in existing data, as opposed to human composition, which can draw from lived experiences and nuanced understanding. If not handled carefully, this can lead to mistakes and a line that damage credibility.
The primary reasons AI content requires QA are as follows:
1. Factual Accuracy Risks
AI tools often attending information confidently, even when it is wrong. For instance, a model might misquote statistics, misstate dates, or invent nonextant studies. Without verification, such errors can misguide readers and damage trust.
2. Brand and Tone Misalignment
AI generated text may sound too formal, too casual, or at odds with brand name voice. For constitution that have spent years building a distinct tone, even small deviations can confuse audiences and dilute brand operator.
3. SEO and Engagement Concerns
Search engines increasingly prioritize high AI Content quality, authentic content. AI outputs that lack depth, ability, or relevance may perform poorly in rankings. Additionally, content that feels robotic or repetitive can disengage readers, reducing edition and loyalty.
4. Lawful and Ethical Implications
AI content can unintentionally plagiarize existing material or reproduce biases hidden in its training data. Businesses that publish such easygoing risk legal challenges and reputational damage.
5. The Hallucination Problem
One particular problem is AI hallucinations, which occur when the system produces inaccurate but plausible information. For instance, misattributing quotes or citing reports that don’t exist. In the absence of a QA procedure, these problems go unnoticed.
QA is essentially a safety net. It guarantees that, without compromising dependability, AI generated content fulfills the promises of speed and scale. Businesses safeguard their audience’s trust as well as their reputation by incorporating quality checks.
Key Elements of an Effective QA Process
4.1 Accuracy and Factual Correctness
Every claim, statistic, or mention must be verified. This often definite quantity fact checking with trusted databases, cross-index industry reports, or using fact checking tools. A “trust but verify” approach is vital.
4.2 Consistency in Tone and Style
Readers expect a agreeable experience across all brand communications. QA teams check for tone alignment whether the content feels cordial, professional, or important so every piece reflects the brand personality.
4.3 Relevance to Audience and Intent
Good content speaks straightaway to the audience’s needs. QA involves checking whether the piece addresses the right pain points, answers communal questions, and delivers actionable value. Content should always tie back to the conscious business goal be it education, lead generation, or engagement.
4.4 Compliance with Brand and Legal Standards
AI may unwittingly use phrasing that struggle with legal requirements or industry regulations. QA ensures compliance with right of first publication rules, trademark usage, and data privacy standards. It also safeguards against unintentional plagiarism.
4.5 Detecting and Reducing AI Hallucinations
Particular care is taken to identify false claims. This could entail requiring citations for each factual statement, using AI hallucination detection tools, or manually verifying facts. The likelihood of publishing misleading content is decreased by a multi layered strategy.
These components work together to create a solid QA process that guarantees AI generated content satisfies human standards for usefulness and trustworthiness.
Benefits of a Structured QA Framework
5.1 Improved Trust and Credibility
Gathering engage more when they know they can rely on your contented. Consistent accuracy builds long term trust, positioning a brand as a reliable authorization.
5.2 Time and Cost Efficiency
While QA may sound time consuming, it volcano costly mistakes like retracting content, correcting misinformation, or manual labor reputation fallout. In the long run, structured QA saves root.
5.3 Better User Engagement and SEO Outcomes
High quality self satisfied naturally earns more sound, shares, and backlinks. By aligning QA with SEO practices such as keyword accuracy, ability, and readability Market name boost both engagement and rankings.
How to Build an AI Content QA Process
6.1 Define Quality Benchmarks
Start by establishing what “quality” means for your organization. This might include readability scores, factual accuracy levels, tone of voice guides, or SEO performance metrics.
6.2 Establish Review Workflows
Set up clear stages: initial AI draft → automated checks → human review → final approval. Define who reviews what, and when, to avoid bottlenecks.
6.3 Use Hybrid Review (Human + AI Tools)
Combine the efficiency of AI tools (grammar checkers, plagiarism detectors) with human oversight for nuanced decisions. For example, humans ensure tone is empathetic, while AI spots spelling mistakes instantly.
6.4 Set Up Feedback Loops for Model Improvement
Track recurring errors and feed them back into the AI system. For example, if the model consistently misuses industry jargon, retrain it with corrected examples.
6.5 Monitor and Refine Processes Over Time
QA is never “one and done.” As AI evolves, so should your processes. Regularly audit the framework, update tools, and refine workflows for ongoing improvement.
A well built process not only prevents problems but also strengthens long-term efficiency and reliability.
Tools and Technologies for AI Content QA
7.1 Grammar and Style Checkers
Tools like Grammarly or Hemingway highlight grammar issues, tone mismatches, and readability concerns. They provide a fast first layer of review.
7.2 Fact-Checking and Plagiarism Tools
Platforms like Copyscape, Turnitin, or Google Fact Check Explorer help ensure originality and accuracy. They safeguard against duplication and misinformation.
7.3 AI Bias Detection Tools
Bias can creep into AI-generated text subtly. Tools such as Fairlearn or Aequitas analyze content for harmful stereotypes or unfair representation.
7.4 Content Scoring and Analytics Platforms
Tools like Clear scope or Surfer SEO score content against competitors, highlighting gaps in keyword usage, depth, and structure. They help align QA with performance goals.

Best Practices for Ensuring Content Reliability
8.1 Balancing Automation with Human Judgment
AI tools are helpful, but they can’t replace human intuition. Always pair automation with human oversight for context sensitive checks.
8.2 Regular Audits of AI Generated Content
Schedule periodic reviews of published content to catch errors that slipped through. This also helps refine the QA process.
8.3 Training Staff on AI Content Oversight
Equip teams with knowledge of AI strengths and weaknesses. Training ensures everyone understands how to spot errors unique to AI.
8.4 Aligning QA with Business Goals
Content QA should support broader objectives like lead generation, authority building, or customer trust. This alignment keeps QA practical and results driven.
Read more: 5 Best AI Tools for Content Creators in 2025
Challenges in AI Content QA and How to Overcome Them
9.1 Managing High Content Volumes
Automation tools can handle bulk grammar and plagiarism checks, leaving humans free for strategic reviews.
9.2 Dealing with Rapid AI Updates
Stay informed on AI tool updates and adjust QA processes accordingly. Consider quarterly reviews to update benchmarks.
9.3 Avoiding Over Reliance on Automation
Automation is efficient, but over reliance risks missing nuanced issues. Strike a balance with layered human checks.
9.4 Handling Ethical and Bias Concerns
Bias mitigation requires active monitoring. Adopt bias detection tools and establish editorial standards that prioritize fairness and inclusivity.
Read more: I Tested 50+ AI Tools – These are the TOP 6 for Content Creators
Future of AI Content Quality Assurance
AI content’s future Deeper human-machine integration is the focus of QA. QA will change from “fixing errors” to “guiding creativity” as AI becomes more complex. As content is created, AI tools may soon provide real-time fact checking, bias detection, and brand compliance.
Human oversight will continue to be crucial, particularly in fields that call for strategic insight, ethical judgment, or empathy. Companies that invest in hybrid QA systems now will be better equipped to face the challenges of the future, where reliability and speed must coexist.
Read more: AI Adoption Change Management Strategies Top 7 Proven
Frequently Asked Questions
11.1 What is the difference between human and AI content QA?
Human QA relies on intuition, context, and deep subject knowledge, while AI QA uses algorithms to spot patterns and errors. Together, they create a stronger review system.
11.2 How often should AI-generated content be reviewed?
Every piece should go through QA before publishing. For evergreen content, conduct periodic audits to ensure accuracy over time.
11.3 Can AI fully replace human editors in QA?
No. AI can handle repetitive tasks, but humans are needed for context, tone, and ethical oversight.
11.4 What tools are best for fact-checking AI content?
Google Fact Check Explorer, Copyscape, and Turnitin are commonly used, though industry-specific databases may be needed for specialized content.
11.5 How do businesses measure content quality at scale?
They use a mix of content scoring tools, SEO performance metrics, readability scores, and engagement analytics.
11.6 How can QA processes improve SEO performance?
By ensuring originality, accuracy, and readability, QA directly boosts rankings and reduces penalties from search engines.
11.7 What are the risks of skipping AI content QA?
Risks include reputational damage, misinformation, SEO penalties, and potential legal issues.
11.8 How can teams train for effective QA oversight?
Offer workshops on AI strengths/limitations, provide guidelines for spotting hallucinations, and use case studies for hands-on learning.

